We are excited to announce the launch of Avail's new data attestation bridge on our Kate testnet – an important tool designed to help enable Validium and Volition modes for the ZK and optimistic rollup stacks in the blockchain space. These scaling solutions move transaction data off-chain, offering significant cost reductions compared to rollups and have the potential to add alternative options for developers and users of Layer 2 (L2) and Layer 3 (L3) blockchain solutions.
The true power of Validiums and Volitions lies in their ability to shift data availability off-chain, which significantly cuts the costs of data availability. This is a major stride forward, especially when you consider that up to 70-85% of rollup costs today are attributed to the need for these scaling solutions to make sure data is always available.
What sets Avail's data attestation bridge apart is its flexibility. The bridge is designed to plug into any EVM compatible chain, making it a highly versatile tool in an ever-growing blockchain ecosystem. This broad utility offers limitless possibilities for integrating and connecting blockchain solutions.
And yet, the introduction of the data attestation bridge does more than just enable Validum and Volition modes and reduce operational costs. It sets the stage for a paradigm shift in how we perceive and utilize L2 solutions. As L3 solutions transition into Validiums, their dependence on L2s evolves. Instead of being one of many scaling solutions for a base layer, L2s have the potential to grow into their own ecosystems - becoming liquidity hubs and expanding their role in the blockchain landscape.
This is the beginning of an exciting journey, one that enhances the practicality of today's solutions and sets the stage for the blockchain ecosystem of tomorrow. Buckle up and join us as we delve deeper into this transformation.
Cost-Efficiency for L2 Solutions
The problem of data availability cost not only affects the economic viability of L2 solutions, but also inhibits their ability to scale and serve larger user bases. This is a fundamental roadblock that L2 solutions have grappled with, impeding their full potential for cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
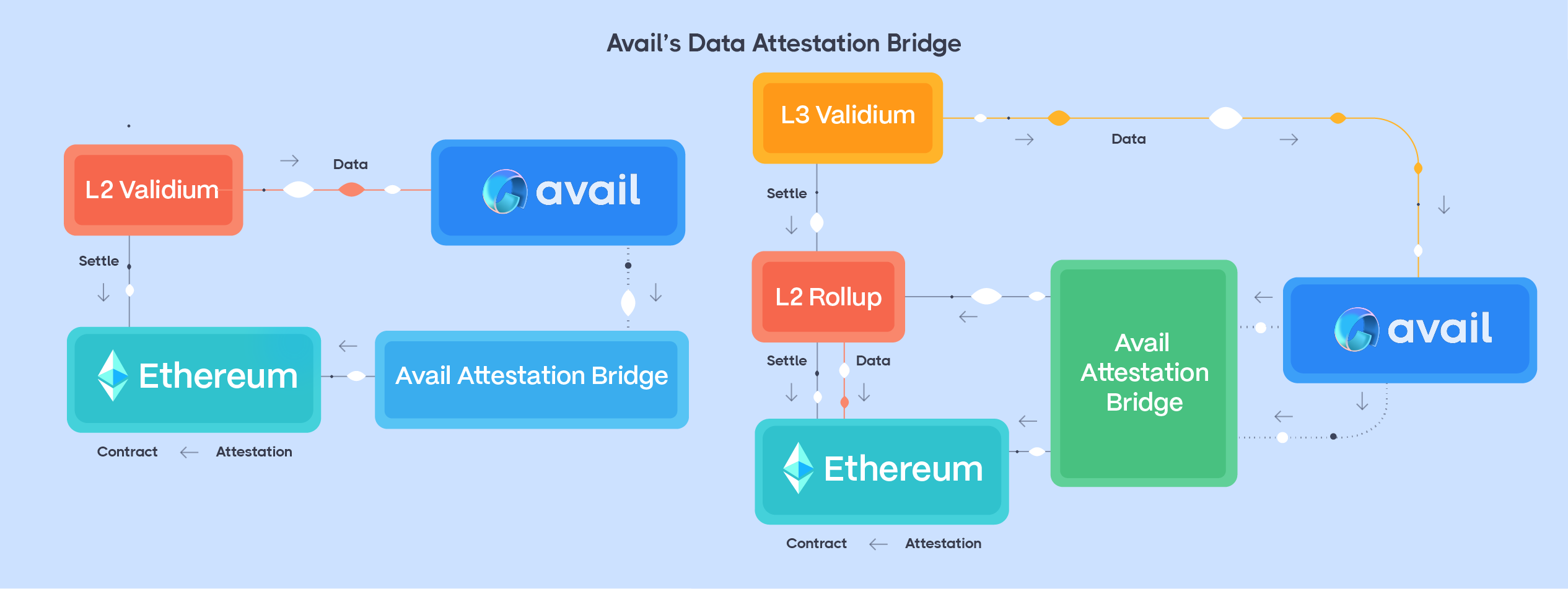
Enter Avail's data attestation bridge. In order to become Validiums and Optimistic chains, rollups post their transaction data or state diffs to Avail while proofs or other metadata are sent to Ethereum. The bridge creates a direct link between the L2 rollup’s data and the L1 via Avail’s off-chain data availability layer. This construction drastically cuts the substantial data availability costs that the L2s of today face, instantly improving the economics of these solutions.
The implications of this transformation are significant. For one, it allows L2 solutions to operate at a much lower cost, making them more attractive to developers and users alike. In addition, by removing the need for on-chain data availability, these solutions can achieve much higher levels of scalability. The result is a more efficient and cost-effective L2 ecosystem, powered by Validiums that fully leverage Avail's off-chain data availability capabilities.
Economic Viability for L3 Solutions
In the absence of an off-chain data availability layer, the construction and operation of L3 solutions becomes an economically challenging task. Traditionally, L3 solutions gather transactions, form execution proofs, and then forward these proofs (along with the accompanying data), to the L2 they reside on. In this setup, the L2 subsequently assumes the responsibility of forwarding that execution proof and its associated data to Ethereum, which carries substantial costs, especially when the L2 aims to inherit Ethereum's security. Given that data availability on Ethereum can account for a large part of an L2's operating cost, this design creates an economic burden that cascades down from the L2 to the L3, rendering the operation of L3 rollups economically challenging, and potentially unsustainable for L2 ecosystems.
Avail’s data attestation bridge introduces a nimble and transformative solution to this economic challenge, enabling L3 rollups to evolve into L3 Validiums. Under this new paradigm, L3 rollups no longer need to send both the proof and data to their L2. Additionally, L2s are not designed for data availability and may have quite weak security assumptions when used without an off-chain data availability layer like Avail. Instead, they can post data directly to Avail and send only the proof to the L2. This alteration in the flow of data and proof significantly reduces the costs associated with operating L3 solutions, making them more economically viable.
Efficiency and Security
In short, Avail maintains its robust data availability model, while the bridge enables efficient attestations from Avail to another chain.
Here’s how it works for an L2 Validium over Ethereum. The same design can be extended for Volitions and L3 solutions:
- Data Publication: An L2 solution publishes transactional data or state diffs as data blobs onto Avail.
- Attestation Creation: A block header on Avail contains two types of attestations. One attestation being KZG polynomial commitments of the submitted data and another being the root of the Merkle tree whose leaves are the data blobs. Supermajority of validators of Avail reach finality over the header by signing over a chain containing the header using the GRANDPA protocol.
- Attestation Bridging: The Data Attestation Bridge then relays the attested Merkle root from Avail to a specific bridge contract on Ethereum, serving as proof that the Avail validators have reached consensus on the data's availability. The KZG commitment is not posted to Ethereum as there is no efficient way to verify KZG openings over BLS12-381 inside EVM. This will be added later.
- Optimistic Verification: Once the attestation is posted to the bridge contract on Ethereum, a waiting period begins during which the attestation is assumed to be valid unless challenged. This is the "optimistic" part of the process. Any party can dispute the attestation during this period if they believe it's incorrect.
- Final Verification on Ethereum: The L2 submits execution proofs corresponding to the state transitions resulting from the transaction data or the state differences. It also shows that there is an attestation of a root containing the data blob over which the execution proof has been generated.
The security model for the current implementation of the bridge is optimistic. The optimistic approach for the bridge allows for a balance between efficiency and security. It speeds up the process of data verification because it does not require every single attestation to be fully checked unless a dispute is raised.
It’s important to note that the optimistic nature of the bridge has no bearing on Avail's function or security. While the bridge optimistically assumes data attestations are valid until challenged, Avail ensures data availability through the use of validity proofs without making any assumptions about the execution correctness of the data.
In addition, the team is also working on a zk-SNARK based data attestation bridge that will eventually replace the optimistic bridge. Do note that the bridge contract interface on Ethereum and other EVM chains will remain the same, ensuring backward compatibility. This means that L2 developers can start using the bridge today on testnet, without worrying about any potential interface changes later.
Building for the Future
In relation to the data attestation bridge, it is worth comparing the level of security different scaling solutions provide. Rollups are widely recognized for offering the highest level of security. On the other hand, Validiums provide a strong level of security, albeit slightly lower on the spectrum. In case of ZK rollups, the integrity of execution is mathematically guaranteed by validity proofs, while the assurance of data ordering and availability is secured by Avail’s consensus mechanism.
Avail is committed to building infrastructure for the future and to empower developers to deliver innovative applications. Our data attestation bridge is part of a long-term vision for a scalable, efficient, and secure blockchain ecosystem. By enabling L2 solutions to step up and become crucial settlement layers, and by laying the groundwork for future advancements with a ZK bridge, Avail is paving the way for the next generation of blockchain technology.
Start building Validiums and Optimistic chains using the bridge today. Follow us on Twitter for updates, announcements, and our not-to-be-missed Twitter Spaces.


